Introduction to Fan in Industrial and Everyday Applications
Fan are the unsung heroes of modern life, working tirelessly to keep us cool, ventilate spaces, and ensure machinery operates efficiently. From the air conditioner humming in your living room to the powerful exhaust system in a factory, fans play a critical role. But not all fans are created equal. Two of the most commonly used types—Axial flow fan and Centrifugal fan—are designed for very different purposes.
Think of Axial fan as the sprinters of the fan world: lightweight, fast, and perfect for moving large amounts of air over short distances. They’re the go-to choice for cooling your laptop or ventilating a warehouse. Centrifugal fan, on the other hand, are more like marathon runners: built for endurance and capable of pushing air through long ducts or against high resistance. Understanding these differences is key to choosing the right fan for your needs.
By understanding these two types of fans—axial flow fan for high-volume, low-pressure applications and centrifugal fans for high-pressure needs—you can better appreciate their unique roles in various industries.
What is Axial flow fan?
An axial flow fan, as the name suggests, moves air or gas in a direction parallel to its axis. Think of it as a propeller on an airplane—its blades rotate around a central hub, creating a pressure difference that propels air forward in a straight line. This design allows axial fans to provide high airflow rates at relatively low pressures, making them ideal for applications such as ventilation and cooling. This simple yet effective design has made axial fans one of the most commonly used fan types across a wide range of industries.
What is a centrifugal fan?
Centrifugal fan operate differently than axial fan, moving air or gas at a 90-degree angle to the direction of the inlet air. Imagine spinning a bucket of water – the centrifugal force pushes the water outward. Similarly, centrifugal fans use this principle to accelerate air radially outward from the impeller. This unique design allows them to produce higher pressures than axial fan, and their rugged construction and ability to operate in harsh conditions make centrifugal fans a must-have for demanding environments. This mechanism makes centrifugal fans particularly effective for applications that require high-pressure airflow.
Basic Definitions and Working Principles
Axial Fan: How Do They Work?
Axial fan operate by moving air along their axis, much like how a propeller pushes air or water. The blades are designed to create a pressure difference that draws in air from one side and expels it out the other in a straight line. This simplicity makes them highly efficient for applications requiring high airflow at low pressure.
- Key Components: Axial fans consist of a central hub with blades that resemble airplane propellers. These blades are angled to maximize airflow while minimizing resistance.
- Applications: Picture the cooling fan in your desktop computer or the exhaust fan in your bathroom—these are classic examples of axial fans at work.
- Design Benefits: Their compact size and straightforward design make them ideal for tight spaces or situations where energy efficiency is a priority.
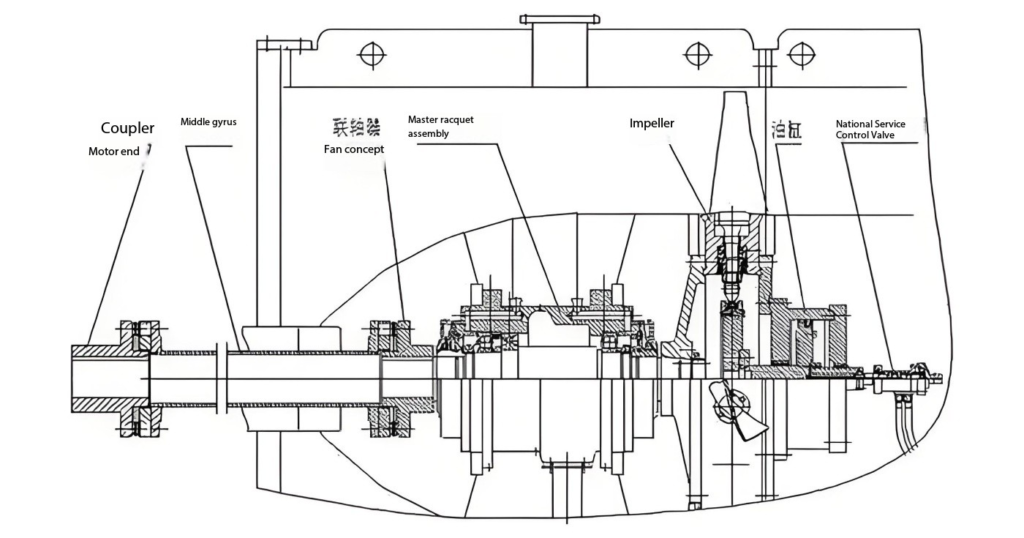
Centrifugal Fan: The Science Behind Them
Centrifugal fan work differently. Instead of moving air straight through, they draw it into an impeller where it’s spun around and expelled at a 90-degree angle. This change in direction allows centrifugal fans to generate much higher pressure than their axial counterparts.
- Key Components: These fans feature an impeller with curved blades (forward-curved, backward-curved, or radial), housed within a volute casing that guides airflow.
- Applications: Imagine an industrial factory where hot gases need to be vented through long ducts—that’s where centrifugal fans shine.
- Design Benefits: Their ability to handle high static pressure makes them indispensable in ducted systems or environments with significant airflow resistance.
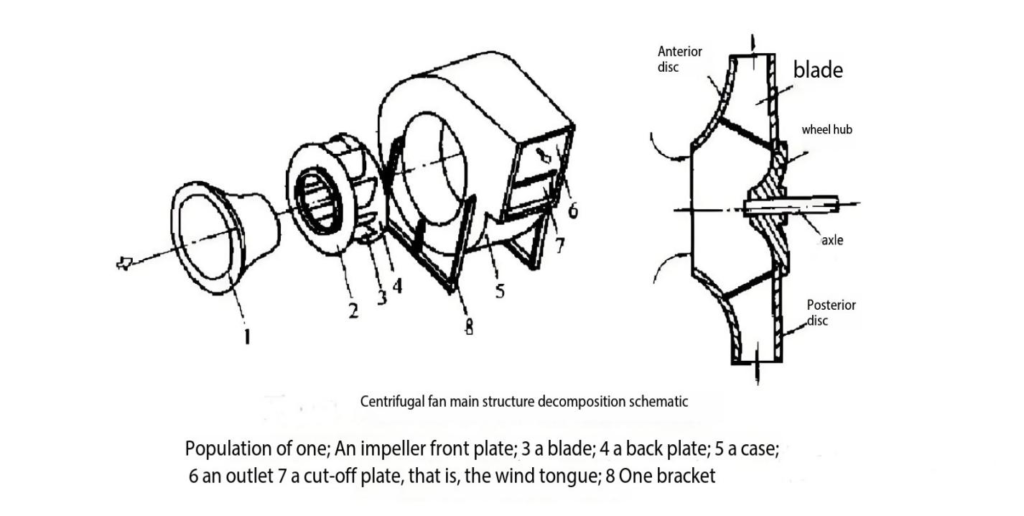
Performance Comparison
Airflow and Pressure
Axial fan excel at moving large volumes of air quickly but struggle when faced with resistance, such as long ducts or filters. Centrifugal fan, by contrast, thrive in high-resistance environments thanks to their ability to generate substantial pressure.
For example, if you’re ventilating an open warehouse, an axial fan is your best bet. But if you’re dealing with an HVAC system that needs to push air through multiple floors of ductwork, a centrifugal fan is the clear winner.
Energy Efficiency
Axial fan are generally more energy-efficient for low-pressure applications because they don’t have to work as hard to move air. However, centrifugal fans become more efficient as resistance increases. This makes them ideal for industrial settings where energy costs can quickly add up.
Noise Levels
Noise is another important consideration. Axial fan tend to be quieter at lower speeds but can become noisy when operating at high RPMs. Centrifugal fan produce steadier noise levels but may emit more sound overall due to their complex airflow patterns.
Durability
When it comes to durability, centrifugal fans take the lead. Their robust design allows them to operate in harsh environments involving dust, debris, or corrosive gases. Axial fan are less rugged but perform exceptionally well in clean, controlled settings like offices or homes.
Application Scenarios
The Strengths of Axial Flow Fan
Axial fan are versatile and widely used across industries:
- Electronics Cooling: Think about the small fan inside your gaming console or laptop that keeps it from overheating during intense use.
- HVAC Systems: These fans are perfect for ventilating large spaces like auditoriums or warehouses.
- Agriculture: Farmers use axial fans to dry grains or ventilate livestock barns.
- Industrial Use: They’re often employed for cooling furnaces or welding operations where high airflow is needed without much pressure.
The Strengths of Centrifugal Fan
Centrifugal fan dominate when high-pressure airflow is required:
- Ducted HVAC Systems: Perfect for moving air through long ducts with filters or dampers.
- Industrial Exhausts: Used in factories to remove hot gases or fumes from processes like metalworking.
- Material Handling: These fans can even transport bulk materials like grain or flour through pneumatic systems.
- Pollution Control: Essential for running filtration systems that remove contaminants from industrial emissions.
Choosing the Right Fan
Selecting between an axial fan and a centrifugal fan boils down to understanding your specific needs:
- Airflow Requirements:
- Need lots of air over a short distance? Go with an axial fan.
- Need high-pressure airflow through ducts? A centrifugal fan is your solution.
- Space Constraints:
- Axial fans’ compact design makes them ideal for tight spaces.
- Centrifugal fans require more room due to their larger size and complex housing.
- Environmental Conditions:
- Axial fans thrive in clean environments like offices.
- Centrifugal models excel in harsh conditions involving dust or corrosive gases.
- Budget Considerations:
- Axial fans are usually cheaper upfront but may have higher maintenance costs over time.
- Centrifugal fans cost more initially but offer greater durability and efficiency in demanding applications.
Summarizing Key Differences
| Feature | Axial Flow Fan | Centrifugal Fan |
|---|---|---|
| Airflow Direction | Parallel to axis | Perpendicular (radial) |
| Pressure Capability | Low | High |
| Energy Efficiency | Better at low resistance | Better at high resistance |
| Noise Levels | Quieter at low speeds | Steadier but potentially louder |
| Durability | Moderate | High |
| Typical Applications | Electronics cooling, HVAC | Ducted HVAC, industrial exhausts |
By understanding these distinctions, you’ll be better equipped to choose the right fan for any application—whether it’s keeping your laptop cool during a gaming marathon or ventilating an entire factory floor.