In the world of industrial ventilation, selecting the right type of fan is crucial for optimizing airflow and system performance. Two common types of axial fans, tube axial and vane axial, are widely used in various applications due to their distinct characteristics and capabilities.
This blog post will delve into the key differences between tube axial and vane axial fans, focusing on their design, airflow direction, airflow rates, pressure capabilities, and efficiency.
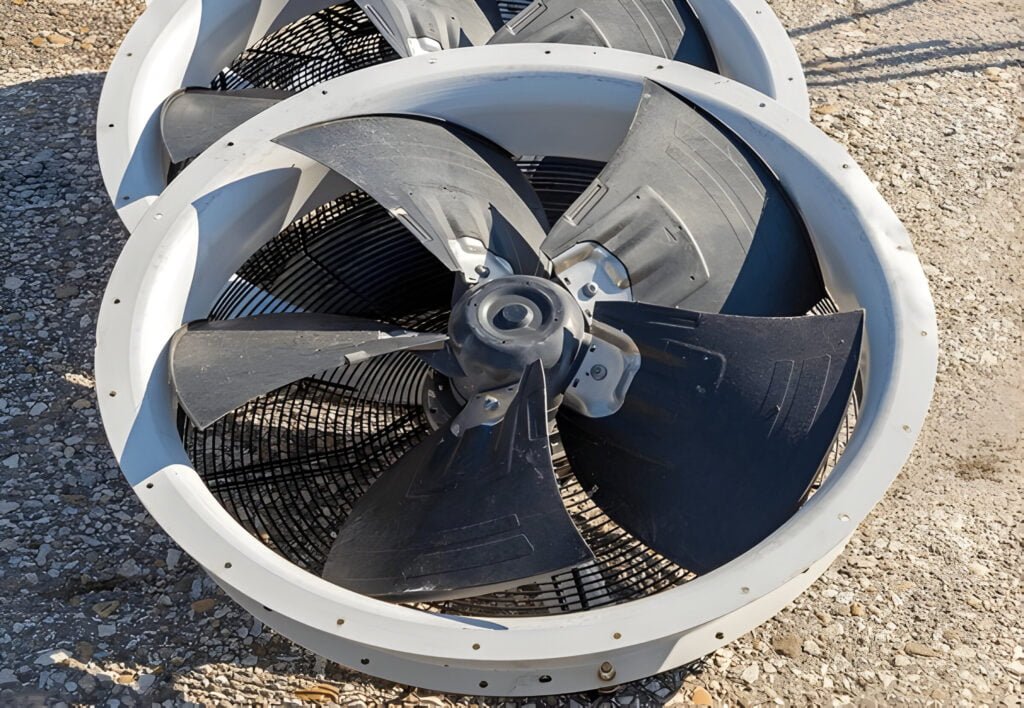

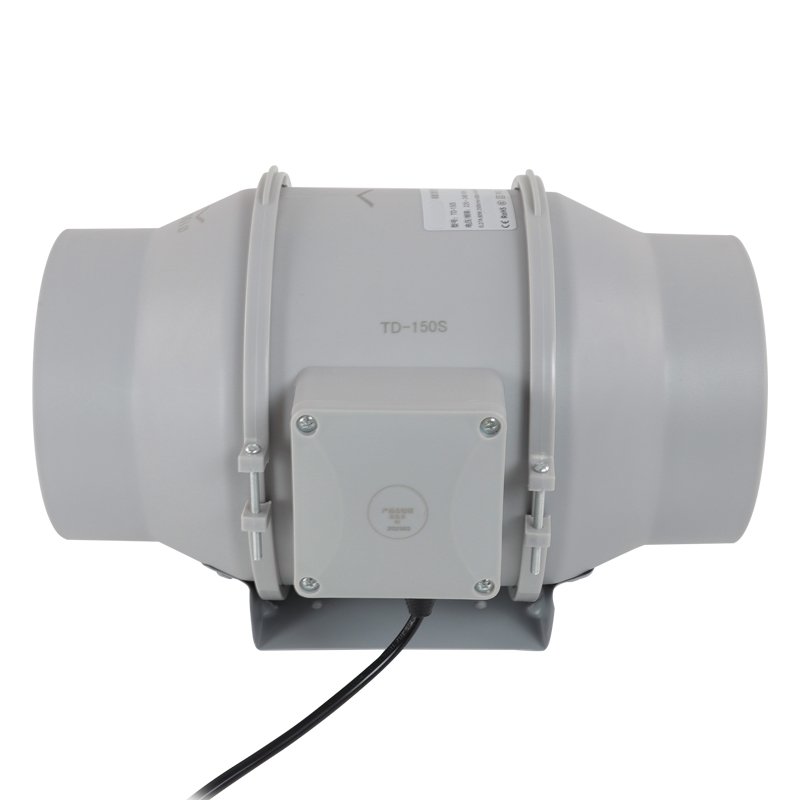
What Is Tube Axial Fan
A tube axial fan is a type of axial flow fan that consists of a propeller or impeller mounted inside a cylindrical tube or housing. The propeller blades are designed to move air in a straight line parallel to the shaft, providing axial airflow. Tube axial fans are known for their ability to move large volumes of air efficiently in a compact design.
What Is Vane Axial Fan
A vane axial fan is another type of axial flow fan that shares many similarities with tube axial fans but incorporates additional components to improve airflow characteristics and performance. The key distinguishing feature of a vane axial fan is the presence of guide vanes or air straighteners, which are located either before or after the impeller.
Vane axial fans are designed to provide high airflow rates and can operate at higher static pressures compared to tube axial fans. The guide vanes help to reduce swirl and turbulence in the airflow, which improves the fan’s efficiency and allows it to generate higher pressures. This makes vane axial fans suitable for applications that require high airflow rates and medium to high static pressures.
Key Difference Between Tube Axial and Vane Axial Fans
Design
Tube axial fans consist of a propeller-shaped blade assembly mounted inside a cylindrical tube or housing. The blades are attached directly to the motor shaft, resulting in a compact, space-efficient design.
Vane axial fans feature a separate fan shaft with guide vanes positioned either before or after the impeller blades. Vane axial fans often have a more complex design compared to tube axial fans, with additional components such as adjustable blade pitch mechanisms and sturdier construction to handle higher pressures.
Airflow Direction
Both tube axial and vane axial fans are designed to move air in a parallel direction to the fan shaft, creating axial airflow. However, the presence of guide vanes in vane axial fans helps to straighten and concentrate the airflow, resulting in a more focused and uniform air stream.
Tube axial fans may experience some swirl and turbulence in the airflow due to the absence of guide vanes. This can lead to a slightly less concentrated airflow pattern compared to vane axial fans.
Airflow Rates
Tube axial fans are known for their ability to move large volumes of air at relatively low pressures. They are well-suited for applications that require high airflow rates, such as general ventilation, cooling, and exhaust systems. The compact design of tube axial fans allows for efficient air movement in space-constrained environments.
Vane axial fans, with their straightening vanes and more complex design, are capable of achieving higher airflow rates compared to tube axial fans of similar size. The guide vanes help to reduce turbulence and improve the overall efficiency of the fan, enabling it to move more air with less power consumption.
Pressure Capabilities
The guide vanes in vane axial fans help to convert the kinetic energy of the airflow into static pressure, making them suitable for applications that require medium to high-pressure air movement.
Tube axial fans, due to their simpler design and lack of guide vanes, are limited in their pressure capabilities. They are primarily used in low-pressure applications where high airflow rates are the primary requirement.
Efficiency
Tube axial fans, with their straightforward design and direct drive configuration, offer good efficiency in low-pressure, high-volume applications. The absence of additional components like guide vanes reduces friction losses and contributes to their overall efficiency.
Vane axial fans, despite their more complex design, can achieve higher efficiencies compared to tube axial fans in certain applications. The guide vanes help to straighten the airflow, reduce turbulence, and minimize energy losses. This improvement in airflow characteristics translates to better overall efficiency, particularly in medium to high-pressure applications.