Belt-driven blowers are an integral part of many industrial processes, providing a reliable and efficient means of moving air or gases. These mechanical devices consist of a blower wheel connected to a motor via a belt and pulley system, allowing for flexibility in speed control and power transmission.
In this blog post, we will delve into the intricacies of belt-driven blowers, exploring their advantages, disadvantages, and various applications across industries. We will also compare belt-driven blowers with their direct-drive counterparts to help readers make informed decisions when selecting the most suitable blower technology for their specific needs.
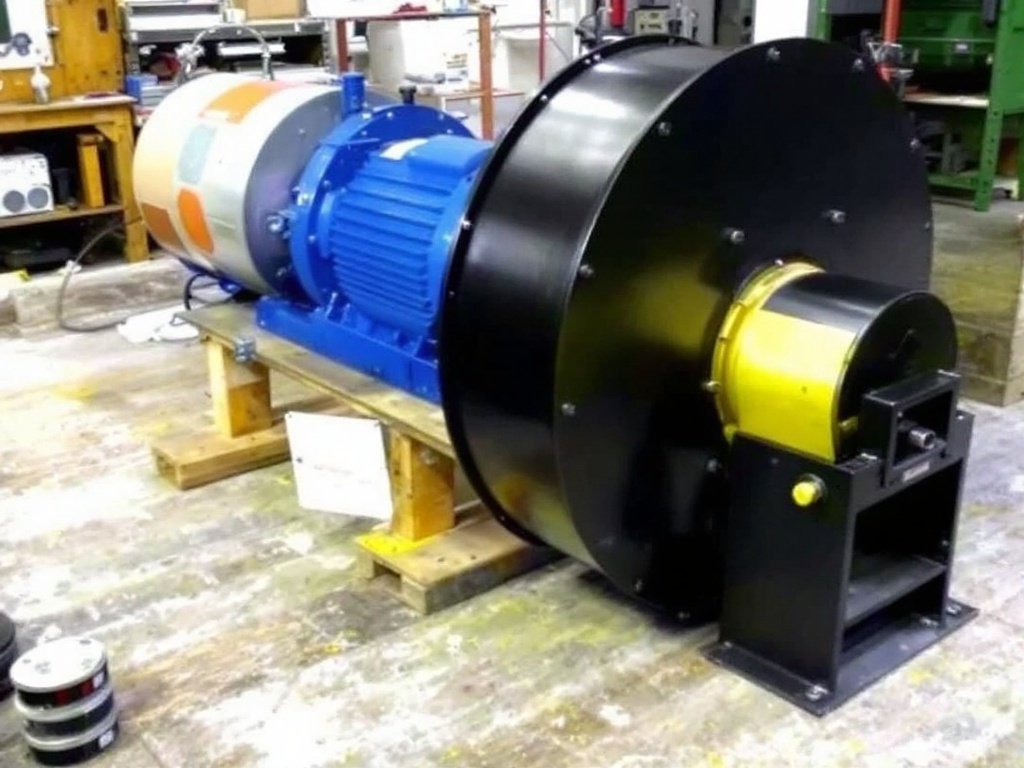
What Is Belt Driven Blower
A belt-driven blower is a type of air-moving device that uses a belt and pulley system to transfer power from the motor to the blower wheel or impeller. The motor drives a pulley, which is connected to another pulley on the blower shaft via a belt. As the motor runs, it rotates the belt, which in turn spins the blower wheel, drawing in air from the inlet and expelling it through the outlet.
Belt-driven blowers are commonly used in various industrial applications where a reliable and efficient source of air flow is required, such as in ventilation systems, dust collection, and pneumatic conveying.
Advantages of Belt-Driven Blowers
Flexibility in Rpm
One of the key advantages of belt-driven blowers is their flexibility in terms of rpm (revolutions per minute). By adjusting the size of the pulleys or using a variable speed motor, the speed of the blower can be easily changed to meet different air flow requirements. This allows for greater control over the blower’s performance and enables it to be adapted to various applications without the need for a complete system overhaul.
Cost Efficiency
Belt-driven blowers are generally more cost-effective than direct-drive blowers, especially for applications that require high volumes of air flow. The belt and pulley system allows for the use of a smaller, less expensive motor to achieve the same air flow as a larger, more costly direct-drive motor. Additionally, the ability to adjust the blower’s speed via pulley changes can help optimize energy consumption, leading to lower operating costs.
Longevity and Reliability
When properly maintained, belt-driven blowers are known for their longevity and reliability. The belt and pulley system acts as a buffer between the motor and the blower, absorbing shock and vibration that could otherwise damage the components. This helps to extend the life of both the motor and the blower, reducing the frequency of repairs and replacements. Furthermore, belts are relatively inexpensive and easy to replace when they do wear out, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
Disadvantages of Belt-Driven Blowers
Maintenance Requirements
While belt-driven blowers are generally reliable, they do require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Belts must be periodically inspected for wear, tension, and alignment, and replaced when necessary. Failing to properly maintain the belt and pulley system can lead to decreased efficiency, increased noise and vibration, and potentially costly breakdowns.
Energy Efficiency
Although belt-driven blowers can be cost-effective, they may not be as energy-efficient as direct-drive blowers in certain applications. The belt and pulley system introduces additional friction and energy losses, which can reduce the overall efficiency of the blower. However, this can be mitigated to some extent by using high-quality, energy-efficient belts and properly sizing the pulleys for the desired air flow.
Dust Generation
In some environments, belt-driven blowers may generate more dust than direct-drive blowers due to the wear of the belts and the friction between the belt and pulleys. This can be a concern in applications where air purity is critical, such as in food processing or pharmaceutical manufacturing. Regular cleaning and maintenance, as well as the use of dust-resistant belts and enclosures, can help minimize this issue.
Applications of Belt-Driven Blowers
Industrial Ventilation
Belt-driven blowers are widely used in industrial ventilation systems to provide fresh air, remove contaminants, and maintain comfortable working conditions. They can be found in factories, warehouses, and other industrial facilities, where they help to control temperature, humidity, and air quality.
Dust Collection
In industries such as woodworking, metalworking, and mining, belt-driven blowers are often used as part of dust collection systems. They create the necessary airflow to capture dust, chips, and other particulates generated during manufacturing processes, helping to maintain a clean and safe work environment.
Pneumatic Conveying
Belt-driven blowers play an important role in pneumatic conveying systems, which use air pressure to move materials through pipes or ducts. These systems are commonly used in industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing to transport powders, granules, and other bulk materials.
Wastewater Treatment
In wastewater treatment plants, belt-driven blowers are used to provide aeration for biological treatment processes. They supply oxygen to the microorganisms that break down organic matter in the wastewater, helping to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of the treatment process.
Comparison with Direct Drive Blowers
| Belt-Driven Blowers | Direct Drive Blowers |
|---|---|
| Belt and pulley system transmits power from the motor to the blower wheel | Motor shaft directly connects to and drives the blower wheel |
| Allows flexibility to alter blower speed/airflow by changing pulley sizes | Blower speed is fixed based on the motor’s set rpm |
| Belts absorb shock and vibration, enabling smoother and quieter operation | Rigid connection transmits more vibration and noise from the motor |
| Belts slip under overload conditions, protecting the motor from damage | Motor is more susceptible to damage from overloading or jams |
| Regular belt tensioning and replacement required to maintain performance | Requires little maintenance beyond lubricating motor bearings |
| Belts, pulleys, and bearings create friction, reducing energy efficiency | Direct motor-blower coupling minimizes frictional losses |
| External belt drive allows mounting the motor away from the airstream | Motor is directly exposed to the conveyed air and any dust/debris |
| Lower upfront cost due to simpler, more standardized components | Higher initial cost for specialized motors and blower wheel hubs |
| Suitable for most general ventilation, exhaust, and conveying applications | Ideal for applications demanding compact size and maximum efficiency |