In the world of ventilation systems, inline fans and exhaust fans are both designed to move air, they differ in their installation, functionality, and performance characteristics.
This blog post will delve into the key differences between inline fans and exhaust fans, exploring their unique features and applications in various settings.
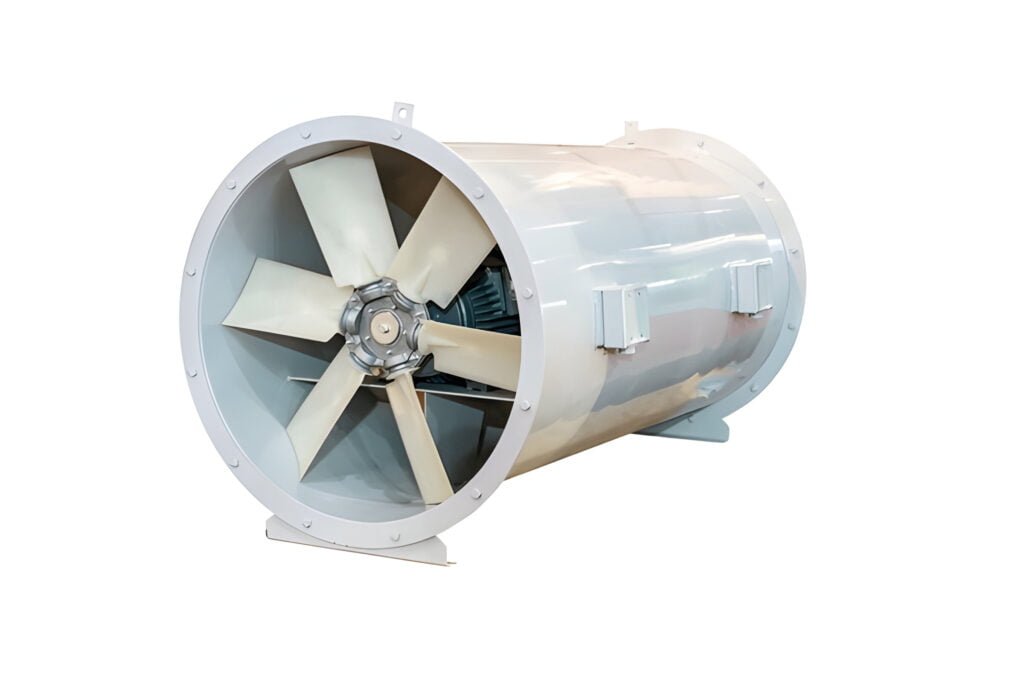

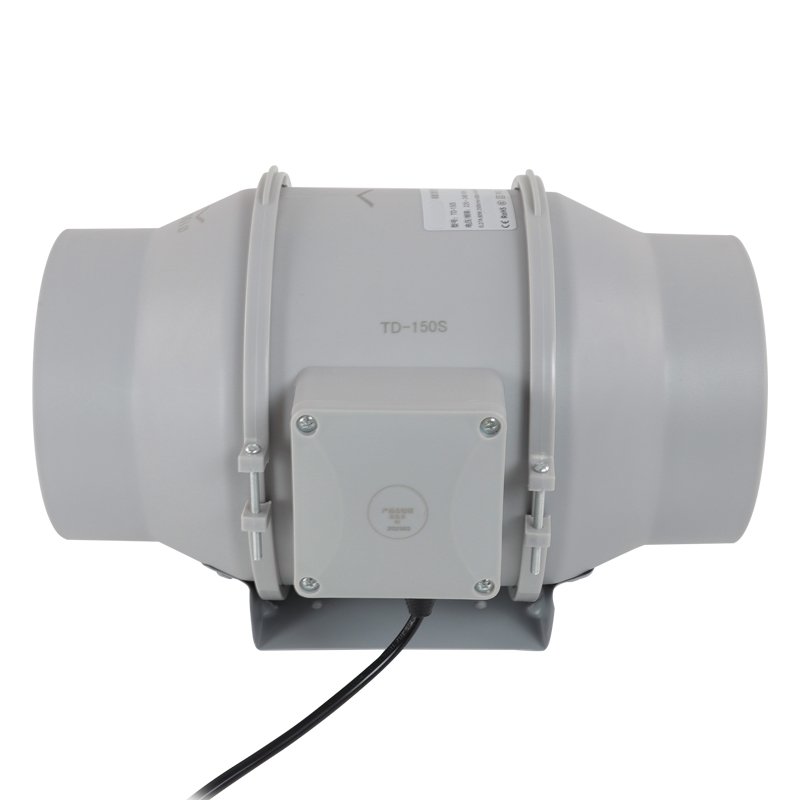
What Is an Inline Fan
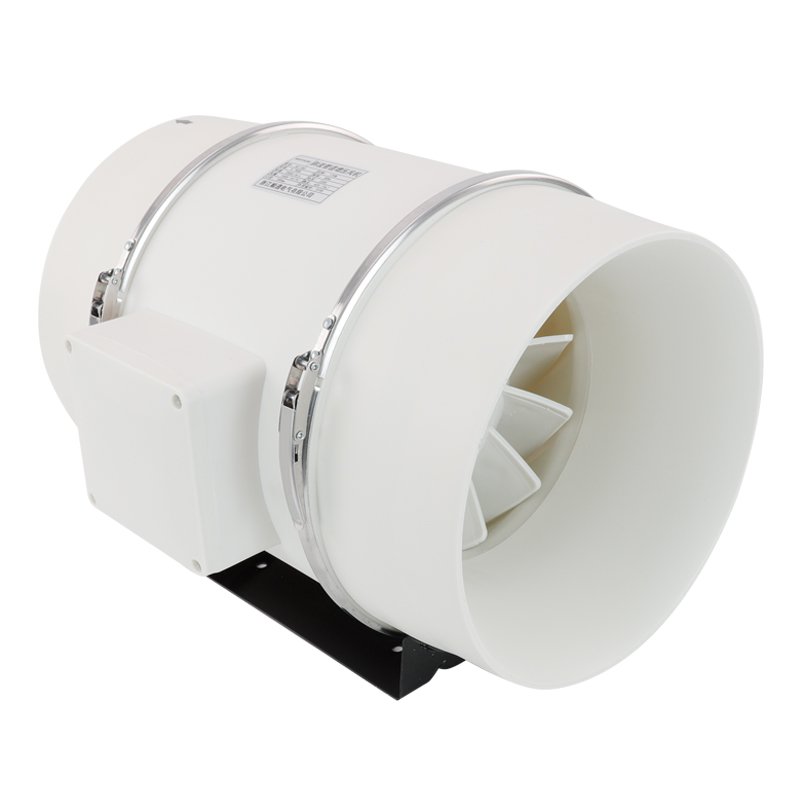
An inline fan, also known as an inline duct fan or a booster fan, is a type of ventilation fan designed for installation within the ductwork of a ventilation system. The primary function of an inline fan is to boost airflow within the ducts, helping to overcome resistance caused by long duct runs, bends, or branches.
Inline fans are commonly used in both residential and commercial spaces to improve indoor air quality, remove excess humidity, and maintain a comfortable living or working environment. They are particularly effective in ventilation systems with complex or extensive ductwork, where a single exhaust fan may not provide sufficient airflow.
How Inline Fans Work
Inline fans operate by drawing air from one or more intake points and pushing it through the ductwork to the exhaust point. The fan is typically mounted within the ductwork using brackets or suspension systems, allowing it to be positioned at any point along the duct run. As the fan operates, it creates a pressure difference within the ductwork, which helps to overcome the resistance caused by the length, bends, and branches of the ducts.
What Is an Exhaust Fan
An exhaust fan is a ventilation device designed to remove stale, humid, or polluted air from an enclosed space and expel it to the outdoors. The primary function of an exhaust fan is to create negative pressure within a room, which allows it to extract air from the space and push it outside through a duct or vent. This process helps to regulate humidity levels, prevent mold growth, and keep the indoor environment comfortable and healthy.
How Exhaust Fans Work
Exhaust fans create negative pressure within the room, which allows fresh air to enter through vents or other openings, promoting proper ventilation.
The primary components of an exhaust fan include the motor, blades, and housing. When the fan is switched on, the motor spins the blades, drawing air from the room into the housing and pushing it out through the exhaust duct. The duct is connected to an exterior vent, typically located on the roof or an external wall, allowing the extracted air to be released outside.

Key Differences Between Inline Fans and Exhaust Fans
While both inline duct fans and exhaust fans serve the purpose of moving air and improving indoor air quality, there are several key differences between these two types of ventilation fans.
Installation and Placement
Inline duct fans are designed to be installed within the ductwork of a ventilation system. They are typically positioned along the length of the ducting, allowing them to boost airflow and overcome static pressure challenges associated with longer duct runs.
Exhaust fans are commonly installed directly on the ceiling, wall, or external wall of the space they are ventilating. Ceiling exhaust fans are often used in bathrooms and kitchens to remove moisture, odors, and other pollutants directly from the room. Wall-mounted exhaust fans are another common placement option, particularly in commercial settings where direct ventilation is required.
Noise Levels
Due to their placement within the ductwork, inline fans tend to produce less noise in the living space compared to exhaust fans. The sound generated by an inline fan is often muffled by the surrounding ductwork.
Exhaust fans, especially those mounted directly on the ceiling or wall, can be more audible in the room they are installed in.
Air Movement
Inline fans are known for their ability to move larger volumes of air over longer distances. They are designed to work in conjunction with the ductwork, effectively overcoming static pressure and ensuring consistent airflow throughout the ventilation system.
Exhaust fans are primarily designed for localized air extraction. They are effective at removing stale air, moisture, and odors directly from the space they are installed in. While exhaust fans can move substantial volumes of air, their airflow capacity is generally limited by the size of the unit and the specific application requirements.
Functionality
Inline fans are designed to boost airflow and distribute air throughout the ductwork. They are commonly used in applications where air needs to be moved over longer distances or through complex ductwork configurations.
Exhaust fans, as the name suggests, are primarily used for extracting air from a specific space. They are effective at removing stale air, moisture, odors, and other pollutants directly from the source. Exhaust fans are commonly installed in bathrooms, kitchens, and other areas where localized ventilation is necessary.
Performance Characteristics
Inline fans are designed to handle higher static pressures and can move larger volumes of air compared to standard exhaust fans.
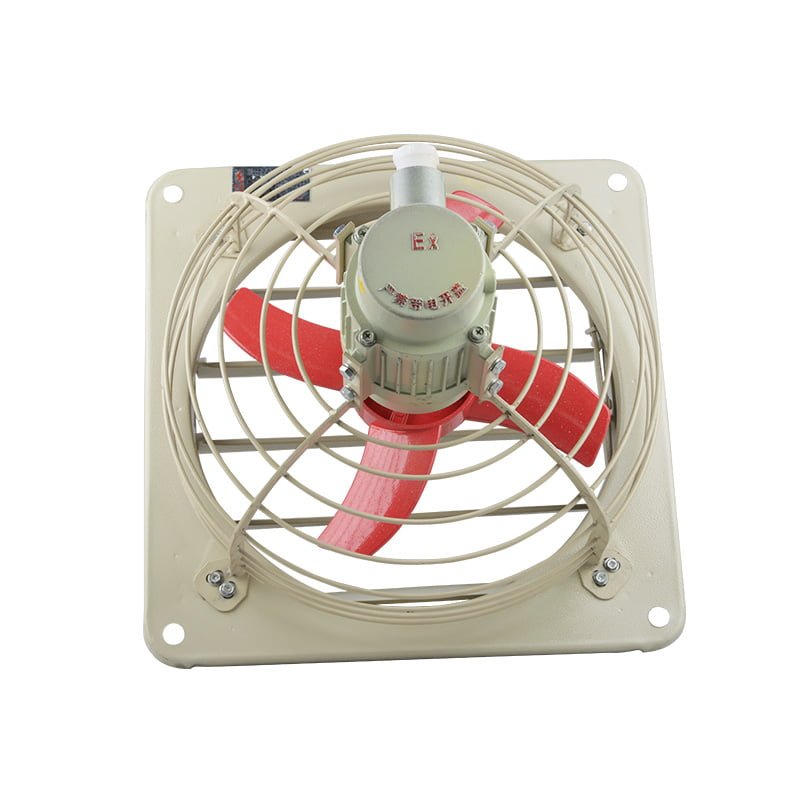

Applications of Inline Fans
- Boosting airflow in HVAC systems
- Improving ventilation in long duct runs
- Overcoming static pressure in ductwork
- Enhancing air circulation in grow rooms and greenhouses
- Assisting in radon mitigation systems
- Supporting ventilation in commercial kitchens
Applications of Exhaust Fans
- Removing moisture and odors from bathrooms
- Ventilating kitchens to remove cooking fumes and heat
- Extracting dust, fumes, and chemicals from workshops and garages
- Cooling attics and reducing heat buildup
- Ventilating laundry rooms to remove excess heat and moisture
- Removing smoke and odors from smoking areas
- Providing ventilation in pet areas to control odors
Can I Use an Inline Duct Fan as an Exhaust Fan?
Yes, an inline duct fan can be used as an exhaust fan in many applications. When used as an exhaust fan, an inline duct fan can effectively remove stale air, moisture, odors, and contaminants from a room or space, helping to improve indoor air quality and maintain a comfortable environment.