Centrifugal fans are essential components in various industrial applications, playing a crucial role in air movement and ventilation. The design of the fan blades, particularly whether they are forward curved or backward curved, significantly impacts the fan’s performance, efficiency, and suitability for specific applications.
In this blog post, we will delve into the distinct characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages of forward curved and backward curved centrifugal fans.

What Is Forward Curved Centrifugal Fan
A forward-curved centrifugal fan is a type of fan that features blades curving in the direction of rotation. This fan type can move a large volume of air at lower pressures. The blades of a forward-curved centrifugal fan are typically shallow and numerous, allowing for efficient operation in a wide range of applications.
Forward-curved centrifugal fans are commonly used in air handling units, heat exchangers, and other HVAC systems. They are particularly well-suited for applications requiring high airflow rates and low to medium pressures, such as clean room ventilation and air conditioning. The fan wheel in a forward-curved design is usually smaller in diameter compared to backward-curved fans, making them ideal for compact installations.
The curved blade design of forward-curved fans allows for a simpler and more cost-effective construction compared to other centrifugal fan types. The blades are typically made from lightweight materials, such as aluminum or plastic, which contributes to their lower cost and easier maintenance. However, the design also results in lower efficiency compared to backward-curved fans, as the airflow experiences more turbulence as it moves through the fan.
Advantages of Forward Curved Centrifugal Fans
High Airflow Capacity
Forward-curved centrifugal fans are known for their ability to move large volumes of air at lower pressures.
Compact Size
Due to the smaller impeller diameter and the forward-curved blade design, these fans can be more compact compared to other centrifugal fan types.
Lower Cost
Forward-curved centrifugal fans are generally more cost-effective than other centrifugal fan types, such as backward-curved fans.
Quieter Operation
Compared to other centrifugal fan types, forward-curved fans typically produce less noise during operation. The lower operating speeds and the smoother airflow through the fan contribute to reduced noise levels. This makes them suitable for applications where low noise is a priority, such as air conditioning systems in commercial facilities and ventilation systems in medical facilities.
Disadvantages of Forward Curved Centrifugal Fans
Lower Efficiency
One of the main drawbacks of forward-curved centrifugal fans is their lower efficiency compared to backward-curved fans.
Limited Pressure Capability
Forward-curved centrifugal fans are not well-suited for applications requiring high static pressure.
Sensitivity to Dust and Debris
The forward-curved blade design can be more susceptible to the accumulation of dust and debris compared to backward-curved fans.
Performance Degradation at Off-Peak Conditions
Forward-curved centrifugal fans may experience performance degradation when operating at off-peak conditions or outside their optimal range.
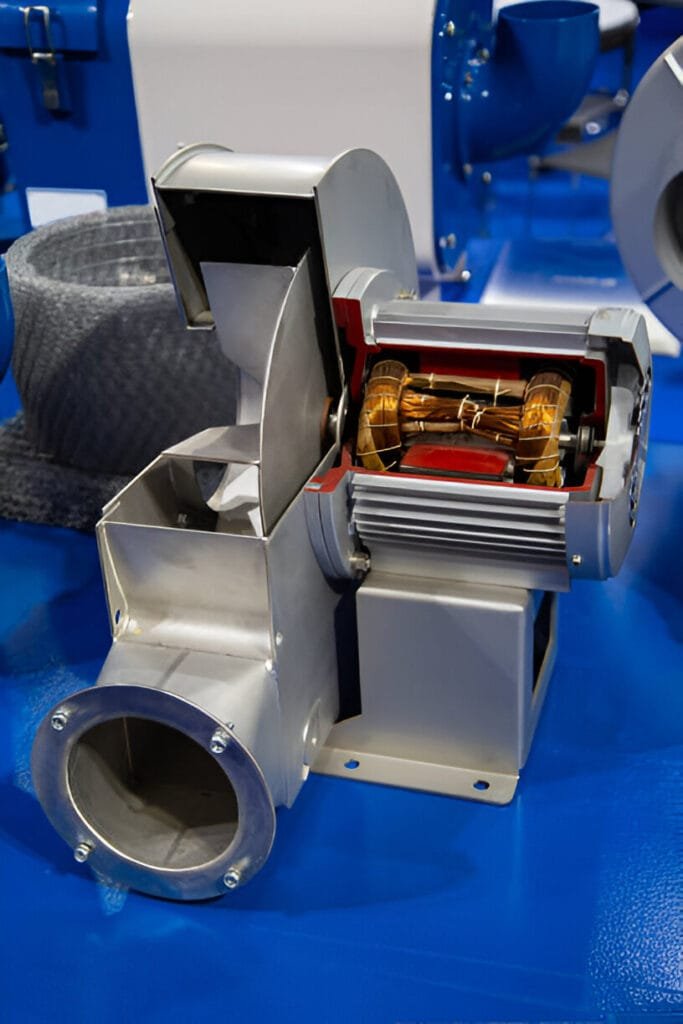

Key Difference Between Forward Curved and Backward Curved Centrifugal Fans
While both types of fans are designed to move large volumes of air, they differ in several key aspects, including blade design, efficiency, airflow characteristics, pressure capabilities, energy consumption, noise levels, and cost.
Blade Design
Forward-curved centrifugal fans feature blades that curve towards the direction of rotation, resembling a hamster wheel. This design allows for a larger number of blades to be fitted on the impeller, resulting in the ability to move larger volumes of air at lower speeds.
Backward-curved centrifugal fans have blades that curve away from the direction of rotation. This blade design is more aerodynamic and efficient, as it minimizes flow disturbances and reduces energy losses.
Efficiency
Backward-curved centrifugal fans generally offer higher efficiency compared to forward-curved ones. The aerodynamic design of backward-curved blades allows for a more efficient transfer of energy from the impeller to the airflow.
Forward-curved centrifugal fans, while less efficient than backward-curved models, still find applications in systems where initial cost is a primary concern, and the operating conditions are less demanding.
Airflow
Forward-curved centrifugal fans excel at moving large volumes of air at lower pressures.
Backward-curved centrifugal fans are designed to deliver moderate to high airflow rates at higher pressures.
Pressure
Backward-curved centrifugal fans are known for their superior pressure capabilities compared to forward-curved models. The aerodynamic blade design allows backward-curved fans to generate higher static pressures.
Forward-curved centrifugal fans, while not as efficient at generating high pressures, still find use in applications where lower pressures are sufficient, such as air circulation and general ventilation.
Energy Consumption
Backward-curved fans, with their higher efficiency and optimized blade design, typically consume less energy for a given airflow and pressure requirement.
Noise Levels
Generally, backward-curved fans operate with lower noise levels compared to forward-curved models. The aerodynamic blade design and efficient airflow generation of backward-curved fans contribute to reduced turbulence and air disturbances, resulting in quieter operation.
Cost
Forward-curved fans tend to have a lower initial purchase cost compared to backward-curved models.